The Future of AI blog series is an evolving collection of posts from the AI Futures team in collaboration with subject matter experts across Microsoft. In this series, we explore tools and technologies that will drive the next generation of AI. Explore more at: Collections | Microsoft Learn
The Future of AI: Vibe Code with Adaptive Custom Translation
In modern software development, boosting productivity while maintaining creativity is key. One emerging approach is vibe coding—a workflow that emphasizes working in a focused, energized state of flow where creativity, momentum, and enjoyment intersect to produce rapid, high-quality outcomes.
In this post, we dive into how this methodology guided the creation of the AdaptCT playground in Azure AI Foundry. You’ll learn how to configure Visual Studio Code with GitHub Copilot to support a productive vibe coding environment, gain actionable tips to maintain flow, and explore the full design process behind the playground solution—including architectural considerations and a complete working code example.
This blog post showcases real-world code examples from enterprise applications and demonstrates practical vibe coding techniques used in production environments.
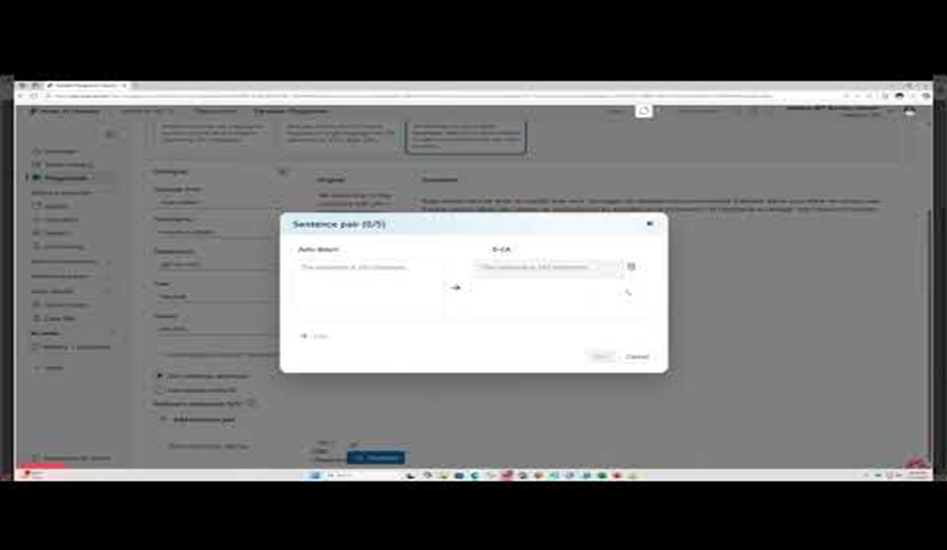
What is Adaptive Custom Translation (AdaptCT)?
Adaptive Custom Translation (AdaptCT) is a translation enhancement feature developed by Microsoft, designed to fine-tune large language model (LLM) outputs—such as GPT-4o from Azure OpenAI in Azure AI Foundry Models—using a small set of reference sentence pairs.
With AdaptCT, users can input up to five manually curated source-target sentence pairs or upload between 5 and 30,000 pre-aligned bilingual segments to create a custom language pair index. During translation, the AdaptCT engine intelligently selects the five most relevant sentence pairs from the index to dynamically adapt the LLM’s output, aligning it more closely with the domain-specific terminology, context, and stylistic requirements of the input text.
The Evolution of Development Paradigms
Traditional development paradigms have followed a predictable pattern:
- Waterfall: Sequential, documentation-heavy
- Agile: Iterative, collaboration-focused
- DevOps: Automation-driven, continuous integration
- Vibe Coding: AI-augmented, conversation-driven, contextually aware
What sets vibe coding apart is its emphasis on maintaining developer flow state while leveraging AI capabilities to handle routine tasks, provide intelligent suggestions, and accelerate problem-solving.
Developing the AdaptCT playground in Azure AI Foundry
Setting Up Your Vibe Coding Environment with VS Code and Copilot
Prerequisites
Before diving into the setup, you’ll need:
- VS Code (latest version)
- Node.js (v22 or higher)
- Yarn (v1.12 or higher)
- GitHub Copilot subscription
Step 1: Installing VS Code Extensions
Install essential extensions for Vibe Coding
code --install-extension GitHub.copilot
code --install-extension GitHub.copilot-chat
code --install-extension ms-vscode.vscode-typescript-next
code --install-extension bradlc.vscode-tailwindcss
code --install-extension ms-playwright.playwright
Step 2: Configuring GitHub Copilot Agent
The Copilot agent acts as your intelligent pair programming partner. Configure it for optimal performance:
// settings.json
{
"github.copilot.enable": {
"*": true,
"yaml": false,
"plaintext": false,
"markdown": true
},
"github.copilot.inlineSuggest.enable": true,
"github.copilot.chat.localeOverride": "en",
"editor.inlineSuggest.enabled": true,
"editor.inlineSuggest.showToolbar": "onHover"
}
Step 3: Setting Up the Development Environment
Create a new project structure optimized for vibe coding:
Initialize project with modern tooling
yarn create vite playground-vibe-coding --template react-ts
cd playground-vibe-coding
# Install Fluent UI and essential dependencies
yarn add @fluentui/react @fluentui/react-components @fluentui/react-icons
yarn add @fluentui/react-hooks @fluentui/react-migration-v8-v9
yarn add styled-components TYPES/styled-components
Development dependencies
yarn add -D @vitejs/plugin-react-swc vite-plugin-svgr typescript
Vite Configuration for Modern Development
Here’s the vite.config.ts that powers enterprise-grade applications:
import react from "@vitejs/plugin-react-swc";
import { defineConfig } from "vite";
import svgr from "vite-plugin-svgr";
export default defineConfig({
plugins: [
react({ tsDecorators: true }),
svgr(),
],
build: {
lib: {
entry: "src/index.tsx",
formats: ["es"],
},
sourcemap: true,
rollupOptions: {
external: ["react", "react-dom"],
},
},
resolve: {
alias: {
"@": "/src",
"@components": "/src/components",
"@utils": "/src/utils",
},
},
server: {
port: 3000,
host: true,
},
});
Building the Playground Solution with Fluent UI
Let’s create a sophisticated component that showcases vibe coding principles. This example is inspired by real enterprise applications - AdaptCT:
Core Component Architecture
// src/components/playground/ReferenceSentences.tsx
import { Stack, TooltipHost } from "@fluentui/react";
import {
Add20Regular,
ArrowRight20Filled,
Delete20Regular,
ErrorCircle20Filled,
Info20Regular,
Warning20Filled,
} from "@fluentui/react-icons";
import { useThemeContext } from "@/context/ThemeContext";
import React from "react";
interface IReferenceSentence {
source: string;
target: string;
}
interface IReferenceSentencesProps {
referenceSentences: IReferenceSentence[];
sourceLanguage?: string;
targetLanguage?: string;
onAdd(source?: string, target?: string): void;
onUpdate(index: number, field: "source" | "target", value: string): void;
onRemove(index: number): void;
}
export const ReferenceSentences: React.FC<IReferenceSentencesProps> = ({
referenceSentences,
sourceLanguage,
targetLanguage,
onAdd,
onUpdate,
onRemove,
}) => {
const { themeStyles } = useThemeContext();
const isDarkMode = themeStyles.theme === "dark";
const [isDialogOpen, setIsDialogOpen] = React.useState(false);
const [sourceSentence, setSourceSentence] = React.useState("");
const [targetSentence, setTargetSentence] = React.useState("");
// Advanced state management for dynamic UI
const [sourceTextareaHeight, setSourceTextareaHeight] = React.useState(40);
const [targetTextareaHeight, setTargetTextareaHeight] = React.useState(40);
const [sourceCharCount, setSourceCharCount] = React.useState(0);
const [targetCharCount, setTargetCharCount] = React.useState(0);
const [hoveredIndex, setHoveredIndex] = React.useState<number | undefined>();
// Refs for advanced DOM manipulation
const sourceResizeRef = React.useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
const targetResizeRef = React.useRef<HTMLDivElement>(null);
// ResizeObserver for dynamic height adjustment
React.useEffect(() => {
const sourceContainer = sourceResizeRef.current;
if (!sourceContainer || !isDialogOpen) return;
const resizeObserver = new ResizeObserver(entries => {
for (const entry of entries) {
setSourceTextareaHeight(entry.contentRect.height);
}
});
resizeObserver.observe(sourceContainer);
return () => resizeObserver.disconnect();
}, [isDialogOpen]);
const handleAddClick = React.useCallback(() => {
setIsDialogOpen(true);
setSourceTextareaHeight(40);
setTargetTextareaHeight(40);
}, []);
const truncateText = React.useCallback((text: string, maxLength = 10): string => {
return text.length <= maxLength ? text : `${text.substring(0, maxLength)}...`;
}, []);
return (
<>
<Stack.Item>
<div style={{ display: "flex", alignItems: "center", gap: "6px" }}>
<div style={{
color: isDarkMode ? "white" : "#242424",
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: "Segoe UI",
fontWeight: "600"
}}>
Reference sentences ({referenceSentences.length}/5)
</div>
<TooltipHost content="Source and target are used to optimize translation with LLM using few shot learning.">
<Info20Regular
style={{
color: isDarkMode ? "white" : "#242424",
fontSize: "16px",
cursor: "pointer",
}}
/>
</TooltipHost>
</div>
{/* Add sentence pair button */}
{referenceSentences.length < 5 && (
<Stack
horizontal={true}
verticalAlign="center"
horizontalAlign="start"
styles={{
root: {
height: "35px",
width: "65%",
border: "1px solid lightgray",
borderRadius: 4,
marginTop: "8px",
padding: "0 8px",
cursor: "pointer",
},
}}
onClick={handleAddClick}
>
<Add20Regular
style={{
color: isDarkMode ? "white" : "black",
fontSize: "20px",
marginRight: "8px"
}}
/>
<div style={{
color: isDarkMode ? "white" : "#242424",
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: "Segoe UI",
fontWeight: "600",
}}>
Add sentence pair
</div>
</Stack>
)}
{/* Display existing sentence pairs */}
{referenceSentences.length > 0 && (
<div style={{
width: "250px",
display: "flex",
flexDirection: "column",
marginTop: "8px",
border: "1px solid lightgray",
borderRadius: 4,
padding: 1,
gap: 6,
fontSize: 14,
fontFamily: "Segoe UI",
}}>
{referenceSentences.map((pair, index) => (
<div
key={`sentence-${index}`}
style={{
height: 32,
background: hoveredIndex === index ? "#F5F5F5" : "white",
display: "flex",
alignItems: "center",
cursor: "pointer",
}}
onMouseEnter={() => setHoveredIndex(index)}
onMouseLeave={() => setHoveredIndex(undefined)}
>
{/* Source text */}
<div style={{ flex: 1, padding: "0 6px" }}>
{truncateText(pair.source)}
</div>
{/* Arrow icon */}
<ArrowRight20Filled style={{ color: "#BDBDBD", margin: "0 4px" }} />
{/* Target text */}
<div style={{ flex: 1, padding: "0 6px" }}>
{truncateText(pair.target)}
</div>
{/* Delete button */}
<button
onClick={(e) => {
e.stopPropagation();
onRemove(index);
}}
style={{
background: "transparent",
border: "none",
cursor: "pointer",
padding: 4,
}}
>
<Delete20Regular style={{ color: "#424242", fontSize: "16px" }} />
</button>
</div>
))}
</div>
)}
</Stack.Item>
</>
);
};
Vibe Coding Tips: Mastering AI-Human Collaboration
1. Conversational Prompt Engineering
When working with Copilot agent, structure your requests like you’re talking to a knowledgeable colleague:
❌ Poor Vibe:
"Make component"
✅ Great Vibe:
"Create a React component called UserProfile that displays user information with Fluent UI styling. Include avatar, name, email, and role. Make it responsive and support both light and dark themes. Add hover effects and proper accessibility."
2. Context-Rich Development
Vibe coding thrives on context. Provide: what you’re building; why you need it; how it fits into the larger system; constraints or requirements.
Example:
"I need to refactor this ReferenceSentences component to support real-time
validation. The component is part of a translation playground where users
input sentence pairs for few-shot learning. It should validate character
limits, show warnings, and prevent invalid submissions."
3. Iterative Refinement
Embrace the iterative nature of vibe coding:
Developer: "The dialog feels cramped. Can we improve the spacing and make
it more visually appealing?"
AI: *Suggests improvements to padding, margins, and visual hierarchy*
Developer: "Great! Now add a gradient background to the header and make
the close button more prominent."
AI: *Implements visual enhancements*
Developer: "Perfect! Let's also add smooth animations for the dialog
open/close transitions."
4. Leveraging AI for Complex Logic
Use AI to help with intricate functionality:
// Example: Complex state management that AI helped optimize to restrict reference sentences
const useReferenceSentenceManager = () => {
const [sentences, setSentences] = React.useState<IReferenceSentence[]>([]);
const [editingIndex, setEditingIndex] = React.useState<number | undefined>();
const addSentence = React.useCallback((source: string, target: string) => {
if (sentences.length >= 5) return false;
setSentences(prev => [...prev, { source: source.trim(), target: target.trim() }]);
return true;
}, [sentences.length]);
const updateSentence = React.useCallback((
index: number,
field: keyof IReferenceSentence,
value: string
) => {
setSentences(prev => prev.map((sentence, i) =>
i === index ? { ...sentence, [field]: value.trim() } : sentence
));
}, []);
const removeSentence = React.useCallback((index: number) => {
setSentences(prev => prev.filter((_, i) => i !== index));
if (editingIndex === index) {
setEditingIndex(undefined);
}
}, [editingIndex]);
return {
sentences,
editingIndex,
setEditingIndex,
addSentence,
updateSentence,
removeSentence,
};
};
Advanced Vibe Coding Patterns
1. Contextual Component Development
When building components, use this conversational pattern:
"I'm building a translation playground component. Users need to add reference
sentence pairs (source → target) for few-shot learning. The component should:
- Support up to 5 sentence pairs
- Show character count with warnings at 250 chars
- Have inline editing capabilities
- Use Fluent UI design system
- Support dark/light themes
- Include proper accessibility features
- Have smooth animations and hover states
The existing codebase uses @fluentui/react v8 with some v9 components mixed in."
2. Progressive Enhancement
Start with basic functionality and progressively enhance:
// Phase 1: Basic structure (AI helps scaffold)
interface BasicProps {
items: string[];
onAdd: (item: string) => void;
}
// Phase 2: Enhanced with validation (AI adds complexity)
interface EnhancedProps extends BasicProps {
maxItems: number;
validator: (item: string) => boolean;
onValidationError: (error: string) => void;
}
// Phase 3: Full-featured (AI integrates advanced patterns)
interface AdvancedProps extends EnhancedProps {
editMode: boolean;
onEdit: (index: number, newValue: string) => void;
customRenderer?: (item: string, index: number) => React.ReactNode;
accessibility: {
ariaLabel: string;
announcements: boolean;
};
}
3. Error Handling and Edge Cases
Vibe coding excels at handling edge cases through conversation:
"This component needs bulletproof error handling. Consider these scenarios:
- User pastes text exceeding character limit
- Network fails during save
- Invalid characters in input
- Rapid clicking causing race conditions
- Screen reader compatibility
- Mobile touch interactions"
Real-World Example: AdaptCT Playground
Here’s how a typical vibe coding session might look when building a translation playground:
Initial Request
"Create a comprehensive translation playground component for an Azure AI Foundry application. It should allow users to:
1. Select source and target languages
2. Add reference sentence pairs for few-shot learning or use dataset index ID (created with custom translation in Azure AI Foundry)
3. Input text to translate
4. See real-time translation results
5. Support both light and dark themes
6. Use enterprise-grade Fluent UI components"
AI Response Structure
The AI would provide component architecture suggestions, TypeScript interfaces, Fluent UI implementation, state management patterns, and accessibility considerations.
Iterative Refinement
Developer: "The reference sentences component looks great! Can we add
drag-and-drop reordering and better validation feedback?"
AI: *Implements drag-and-drop with react-beautiful-dnd and enhanced validation*
Developer: "Perfect! Now let's add keyboard shortcuts and improve the
mobile experience."
AI: *Adds keyboard navigation and responsive design improvements*
Integration with Modern Development Workflows
Package.json Configuration
Our enterprise setup leverages modern tooling:
{
"name": "vibe-coding-playground",
"scripts": {
"dev": "vite",
"build": "vite build",
"preview": "vite preview",
"test": "jest",
"lint": "eslint . --ext ts,tsx --report-unused-disable-directives --max-warnings 0",
"type-check": "tsc --noEmit"
},
"dependencies": {
"@fluentui/react": "^8.122.11",
"@fluentui/react-components": "^9.55.1",
"@fluentui/react-icons": "^2.0.261",
"react": "^17.0.2",
"react-dom": "^17.0.2",
"styled-components": "^5.3.11"
},
"devDependencies": {
"@vitejs/plugin-react-swc": "^3.10.1",
"typescript": "^5.3.3",
"vite": "^4.5.14"
}
}
TypeScript Configuration
{
"compilerOptions": {
"target": "ES2020",
"useDefineForClassFields": true,
"lib": ["ES2020", "DOM", "DOM.Iterable"],
"module": "ESNext",
"skipLibCheck": true,
"moduleResolution": "bundler",
"allowImportingTsExtensions": true,
"resolveJsonModule": true,
"isolatedModules": true,
"noEmit": true,
"jsx": "react-jsx",
"strict": true,
"noUnusedLocals": true,
"noUnusedParameters": true,
"noFallthroughCasesInSwitch": true,
"baseUrl": ".",
"paths": {
"@/*": ["src/*"],
"@components/*": ["src/components/*"]
}
},
"include": ["src"],
"references": [{ "path": "./tsconfig.node.json" }]
}
Performance Optimization in Vibe Coding
Intelligent Code Splitting
// AI-suggested lazy loading pattern
const ReferenceSentences = React.lazy(() =>
import('./components/ReferenceSentences').then(module => ({
default: module.ReferenceSentences
}))
);
const TranslationPlayground: React.FC = () => {
return (
<React.Suspense fallback={<div>Loading...</div>}>
<ReferenceSentences {...props} />
</React.Suspense>
);
};
Memorization Strategies
// AI helps identify optimal memorization points
const MemoizedSentenceList = React.memo<SentenceListProps>(({ sentences, onEdit, onRemove }) => {
return (
<div>
{sentences.map((sentence, index) => (
<MemoizedSentenceItem
key={`${sentence.source}-${sentence.target}`}
sentence={sentence}
index={index}
onEdit={onEdit}
onRemove={onRemove}
/>
))}
</div>
);
}, (prevProps, nextProps) => {
return (
prevProps.sentences.length === nextProps.sentences.length &&
prevProps.sentences.every((prev, index) => {
const next = nextProps.sentences[index];
return prev.source === next.source && prev.target === next.target;
})
);
});
Testing in the Vibe Coding Era
AI-Assisted Test Generation
// Generated through conversational testing with AI
import { render, screen, fireEvent, waitFor } from '@testing-library/react';
import { ReferenceSentences } from './ReferenceSentences';
describe('ReferenceSentences Component', () => {
const mockProps = {
referenceSentences: [],
onAdd: jest.fn(),
onUpdate: jest.fn(),
onRemove: jest.fn(),
};
it('should display add button when less than 5 sentences', () => {
render(<ReferenceSentences {...mockProps} />);
expect(screen.getByText('Add sentence pair')).toBeInTheDocument();
});
it('should validate character limits', async () => {
const { getByRole } = render(<ReferenceSentences {...mockProps} />);
fireEvent.click(screen.getByText('Add sentence pair'));
const sourceInput = getByRole('textbox', { name: /source/i });
fireEvent.change(sourceInput, {
target: { value: 'a'.repeat(251) }
});
await waitFor(() => {
expect(screen.getByText('The maximum is 250 characters.')).toBeInTheDocument();
});
});
it('should support keyboard navigation', () => {
render(<ReferenceSentences {...mockProps} />);
const addButton = screen.getByText('Add sentence pair');
fireEvent.keyDown(addButton, { key: 'Enter' });
expect(screen.getByRole('dialog')).toBeInTheDocument();
});
});
Recommended Practices for Vibe Coding Teams
1. Establish Conversational Standards
Create team guidelines for AI interaction:
AI Interaction Guidelines
Good Prompts
✅ "Create a React component for user authentication with form validation,
error handling, and accessibility features"
✅ "Refactor this function to use React hooks and improve performance"
✅ "Add comprehensive TypeScript types for this API integration"
Avoid These
❌ "Fix this"
❌ "Make it better"
❌ "Add styling"
2. Code Review Integration
Incorporate AI suggestions into code reviews:
// Reviewer comment: "Consider using the AI to optimize this complex state logic"
// AI-suggested improvement:
const useOptimizedState = () => {
const [state, setState] = React.useState(initialState);
const updateState = React.useCallback((updates: Partial<State>) => {
setState(prev => ({ ...prev, ...updates }));
}, []);
return [state, updateState] as const;
};
3. Documentation-Driven Development
Use AI to maintain living documentation:
/**
* ReferenceSentences Component
*
* A sophisticated component for managing translation reference pairs in AI Studio.
* Supports up to 5 sentence pairs with real-time validation, character counting,
* and accessibility features.
*
* @example
* ```tsx
* <ReferenceSentences
* referenceSentences={sentences}
* sourceLanguage="English"
* targetLanguage="Spanish"
* onAdd={handleAdd}
* onUpdate={handleUpdate}
* onRemove={handleRemove}
* />
* ```
*/
Future of Vibe Coding
As we look toward the future, vibe coding represents more than just a development methodology—it’s a paradigm shift toward more intuitive, efficient, and enjoyable software development. Key trends include:
1. Enhanced Context Awareness
AI agents will understand project context, coding patterns, and team preferences.
2. Multi-Modal Development
Integration of voice commands, visual design tools, and code generation.
3. Predictive Development
AI anticipating developer needs and proactively suggests improvements.
4. Collaborative Intelligence
Seamless handoffs between human creativity and AI capabilities.
Conclusion: Amplifying Flow with Vibe Coding
Vibe coding marks a shift toward more intuitive and efficient software development through human-AI collaboration. By blending tools like VS Code, GitHub Copilot, and vite with conversational workflows, developers can boost productivity without sacrificing creativity or control. The goal isn’t to replace human judgment, but to enhance it—letting AI handle the routine so you can focus on the big picture. Set up your environment, experiment with prompts, and let AI amplify your natural coding flow.
Now it’s your turn to create with Azure AI Foundry
- Check out our GitHub Repository
- Watch our demo on YouTube
- Get started with Azure AI Foundry, and jump directly into Visual Studio Code
- Download the Azure AI Foundry SDK
- Join the Azure AI Foundry Learn Challenge
- Review the Azure AI Foundry documentation
- Keep the conversation going in GitHub and Discord
 Microsoft
Microsoft