To allow Autodiscover to function completely there is an important component in Exchange 2007 Server named Providers. Providers are components that are specifically related to the type of client that is trying to connect and be configured. When the Client Access Server role is installed, by default three providers are created: EXCH, EXPR and WEB. We will here discuss each one. In the second part of this blog post, we will talk about when and if those should be modified.
The Autodiscover Service and Outlook Providers
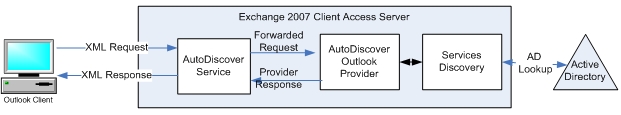
The diagram below explains the role of the Outlook Provider in the Autodiscover process.
When creating or refreshing an Outlook 2007 profile a request is placed to the Autodiscover service; the service determines which provider needs to handle the request. The XML request contains the necessary information for this to happen, such as the SMTP address and which client (MAPI client or Outlook Anywhere) made the request so the Autodiscover service can easily identify the provider the request needs to be forwarded to.
 How does the Autodiscover service know which Outlook client is making the request?
1. The client posts an HTTP(S) request to the Autodiscover service including a XML request.
2. The Autodiscover service parses and validates the request so it knows which provider the request is targeted for. The XML request contains a reference to a schema as the first part of the opening <Autodiscover> XML tag. As you the see in the example bellow the portion "outlook" in the path of the "xmlns=" indicates that a request was made from an Outlook (MAPI) client.
How does the Autodiscover service know which Outlook client is making the request?
1. The client posts an HTTP(S) request to the Autodiscover service including a XML request.
2. The Autodiscover service parses and validates the request so it knows which provider the request is targeted for. The XML request contains a reference to a schema as the first part of the opening <Autodiscover> XML tag. As you the see in the example bellow the portion "outlook" in the path of the "xmlns=" indicates that a request was made from an Outlook (MAPI) client.
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/exchange/autodiscover/outlook/requestschema/2006a"3. If an Outlook Provider cannot be found, the requesting client is notified and the Autodiscover retrieval fails. 4. Once the Autodiscover service has identified the correct provider it will pass the request to it. By default three Outlook Providers are used to configure settings individually for Exchange RPC protocol or internal clients (EXCH), Outlook Anywhere (EXPR) and WEB.
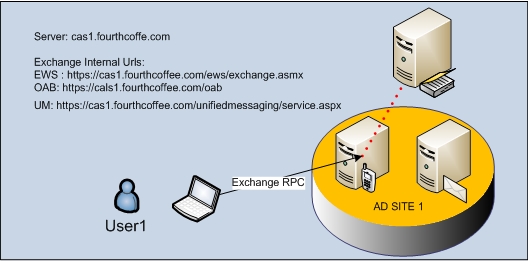
- The EXCH setting references the Exchange RPC protocol that is used internally. This setting includes port settings and the internal URLs for the Exchange services that you have enabled.
- The EXPR setting references the Exchange HTTP protocol that is used by Outlook Anywhere. This setting includes the external URLs for the Exchange services that you have enabled, which are used by clients that access Exchange from the Internet.
- The WEB setting contains the best URL for Outlook Web Access for the user to use. This setting is not in use.
a. If the request is made by an Outlook Exchange RPC client, the EXCH provider will return the InternalUrl configured on the best CAS server for the following services: Availability Service, OAB virtual directory and Unified Messaging virtual directory. http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/library/bb332063.aspx
b. If the request is made by an Outlook Anywhere Exchange HTTP client, the EXPR provider will return the External URL configured on the best CAS server for the same services: Availability Service, OAB virtual directory and Unified Messaging virtual directory and ExternalHostName for Outlook Anywhere.
Note: If the ExternalUrl is not set, the CAS will fail-back returning the InternalUrl.
Note: The Internal and External URL for EWS, OAB and UM can be configured through the following cmdlets: Set-WebServicesVirtualDirectory, Set-OABVirtualDirectory and Set-UMVirtualDirectory respectively. Outlook Providers are global settings in Active Directory The Outlook Providers are global settings in the Active Directory forest, thus there is no need to create an Outlook Provider; however, depending of your environment you might have to tweak their configuration. The Outlook providers settings are in Active Directory, in the following location: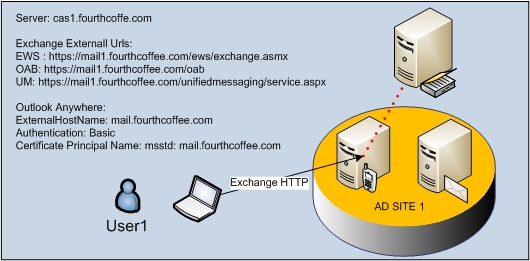
DC=<domain>, CN=Configuration, CN=Services, CN=Microsoft Exchange, CN=<Organization Name>, CN=Client Access, CN=Autodiscover, CN=OutlookCN=EXCH or CN=EXPRIn a few days, I'll cover when and if you should make modifications to those providers. Stay tuned! - Vandy Rodrigues