So - what is WMI? WMI is an implementation of the Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) standard. WMI provides a uniform access mechanism to a vast collection of Windows management data and methods. WMI offers access to this information via script, C++ programming interfaces, dot net classes (system.management), and a command line tool (WMIC). Other WMI capabilities also include eventing, remoting, query, views, user extensions to schema and instrumentation, and more.

Within the architecture of WMI, there are four components we need to consider:
-
Management Applications
-
WMI Infrastructure
-
Providers
- Managed Objects
WMI Management Applications include tools such as the Exchange System Manager. A management application can query, enumerate data, run provider methods or subscribe to events.
The WMI Infrastructure has two components - the WMI Service (winmgmt) including the WMI Core, and the WMI Repository. The WMI repository uses a namespace containing several sub-namespaces that are arranged hierarchically to organize objects. A management application must connect to a namespace before the application can access objects within the namespace. WMI names the namespace root directory as root . The WMI service creates some namespaces such as root\default , root\cimv2 and root\subscription at system startup and pre-installs a default set of class definitions. The WMI service acts as an intermediary between the providers, management applications, and the WMI repository. Only static data about objects is stored in the repository, such as the classes defined by providers. WMI obtains most data dynamically from the provider when a client requests it.
And that brings us to WMI Providers. A WMI Provider is a COM object that monitors managed objects for WMI. A managed object is a component (logical or physical) - such as a hard drive, network card, Operating System or service. A provider supplies WMI with data from an object and handles messages from WMI to the object. A WMI provider consists of a DLL and a Managed Object Format (MOF) file that defines the classes for the provider. WMI classifies providers according to the interface features supplied by the provider. A provider can implement more than one feature:
| Classifications | Description |
| Class | Can supply, modify, delete, and enumerate a provider-specific class. Can also support query processing. Active Directory is a rare example of a service that is a class provider |
| Instance |
Can supply, modify, delete, and enumerate instances of system and provider-specific classes. An instance represents a managed object. Can also support query processing |
| Property | Can supply and modify individual object property values |
| Method | Supplies methods for a provider-specific class |
| Event | Generates event notifications |
| Event Consumer | Maps a physical consumer to a logical consumer to support event notification |
No discussion about WMI Architecture would be complete without a discussion of the Common Information Model (CIM) the and Managed Object Format (MOF) Language. The CIM follows in the steps of object-oriented languages such as C++ and Java. WMI provider developers write their classes in the MOF language - once their classes are constructed in MOF, the developer can supply the class definitions to WMI. This can be done by compiling a MOF file into a binary MOF file (BMF) and giving the BMF files to the Windows Driver Model (WDM) infrastructure. Providers can also compile the MOF's and use the WMI COM API's to provide the WMI Infrastructure with the definitions. Finally, providers can use the MOF Compiler (MOFComp.exe) to add the classes to the WMI repository.
OK - now let's tie all of this together by looking at a very simple script that returns the Computer Name and the Amount of RAM installed:
Set objWMIService = GetObject("winmgmts:" & "{impersonationLevel=impersonate}!\\" & strComputer & "\root\cimv2")
Set colSettings = objWMIService.ExecQuery ("Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem")
For Each objComputer in colSettings
Wscript.Echo "System Name: " & objComputer.Name
Wscript.Echo "Total Physical Memory: " & objComputer.TotalPhysicalMemory
Next
So let's walk through this script. In the first line, we set the strComputer value to ".", indicating that we are working with the local machine. In the next line, we connect to the root\cimv2 namespace on the local machine. In line 3, we create the query that we will use to gather our data - "Select * from Win32_ComputerSystem". The Win32_ComputerSystem WMI class has many properties that provide information regarding the machine. Now that we've defined our query, we move into a For Loop that returns the specific values in which we are interested - the Name and the Total Physical Memory - and outputs the results as shown below:
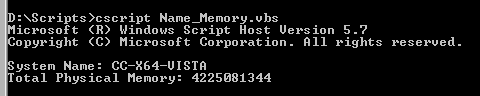
And that wraps up our overview of WMI Architecture. In upcoming posts we will cover WMI troubleshooting - including the use of the WBEMTEST utility and WMI Logging. Until next time ...
Additional Resources:
-
WMI: Introduction to Windows Management Instrumentation
-
WMI Scripting Primer
-
WMI Architecture
-
WMI Providers
-
WMI - Wikipedia Page
-
Web-Based Enterprise Management (WBEM) Standard - DMTF
- Common Information Model (CIM) Standard - DMTF
 Microsoft
Microsoft