Hi, I’m Venkat Bodapati, a software development engineer in Test on the Remote Desktop Virtualization (RDV) team. The purpose of this post is to highlight the key features added and enhancements made in Remote Desktop Gateway (RD Gateway) in Windows Server 2012. To get the most out of this article, you should be familiar with RD Gateway in Windows Server 2008 R2. (For more information about this, see Remote Desktop Gateway Manager ).
In this document, I’ll discuss several changes and improvements to RD Gateway in Windows Server 2012, including:
- Transport changes to enable the WAN improvements in Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) 8.0
- Management console changes to facilitate using these new protocols
- IIS configuration changes
- Load balancing changes to complement the new protocols
In Windows Server 2008 and Windows Server 2008 R2, RD Gateway supports only the RPC over HTTP transport. This is the only transport being used when a client makes an RDP connection via RD Gateway from inside or outside the corporate network.
In contrast, RD Gateway in Windows Server 2012 supports three types of transports: RPC over HTTP, HTTP, and UDP. The following table explains which transports are used when a client connects to various RD Gateway server versions.
|
Client |
RD Gateway Server |
RD Host |
Transport(s) used |
|
Windows Server 2012 |
|
|
|
Windows Server 2012 |
|
|
|
Windows Server 2012 |
Any |
RPC over HTTP |
|
|
Any |
RPC over HTTP |
- The RPC over HTTP transport is for RDP 7.1 and previous clients.
- Beginning with Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, the RDP 8.0 update for Windows 7 SP1, and Windows Server 2008 R2 SP1 (KB 2592687), RDP clients always use HTTP as the default transport, falling back to RPC over HTTP if the pure HTTP transport is not available. The HTTP transport uses the Secure Sockets Layer to establish secure connections between the remote desktop client and the remote desktop server through RD Gateway.
- When connecting to remote desktop servers running Windows 8, Windows Server 2012, or the RDP 8.0 update for Windows 7 SP1 via Windows Server 2012 RD Gateway, UDP connections may be utilized to improve WAN performance. The UDP transport uses a Datagram Transport Layer Security (DTLS) handshake to establish secure connections between the remote desktop client and the remote desktop server through RD Gateway. For more information, see the blog article RemoteFX for WAN: Overview of Intelligent and Adaptive Transports in Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 .
UDP connections can’t be created as stand-alone; UDP connections are established only after a main HTTP connection has been created between the remote desktop client and the remote desktop server. The following table describes the ports being used by different transports in RD Gateway:
|
Transport Type |
Default Port used |
|
HTTP (includes RPC over HTTP) over SSL |
443* |
|
UDP |
3391* |
*These ports are configurable in the RD Gateway management console.
Management Console ChangesIn Windows Server 2012, the RD Gateway server creates three internal connections for each user session: one HTTP connection and two UDP connections. The HTTP connection is used to maintain client communication with the target server, and the two UDP connections are used to support a rich multimedia experience. These three connections can be viewed in the monitoring node of the RD Gateway management console. In the case of Windows Server 2008 R2, only one connection appears for each user session. These changes in Windows Server 2012 will help administrators use the RD Gateway management console to verify that users are able to connect by using appropriate transport protocols.
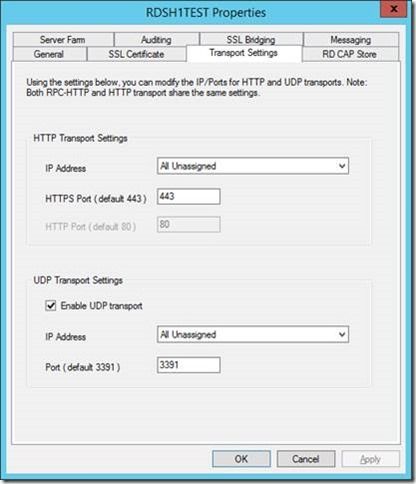
Administrators can make changes to the HTTP and UDP transport settings by using a new tab called Transport Settings that was added to the Properties dialog box in the RD Gateway management console.
IIS Configuration ChangesIn Windows Server 2008 R2, RD Gateway has a strong dependency on Internet Information Services (IIS). Installation of the RD Gateway role creates Rpc and RpcWithCert virtual directories on the IIS default website. It also configures default authentication methods being used to authenticate clients on the IIS server.
In RD Gateway in Windows Server 2012, the IIS configuration is applicable only for clients that are using the RPC over HTTP transport. Any legacy client that requests a connection through RD Gateway in Windows Server 2012 has to use the RPC over HTTP transport. The new HTTP transport doesn’t rely on IIS server; as such, IIS configuration settings will not affect Windows 8 remote desktop clients that request a connection through RD Gateway in Windows Server 2012.
IIS configuration settings continue to be applicable when Windows 8 remote desktop clients request a connection through legacy RD Gateway servers (for example, Windows Server 2008 R2). To use new remote desktop clients with legacy RD Gateway servers, anonymous authentication must be enabled for the IIS default website. Otherwise, client authentication can fail due to the new HTTP transport features. If this is not set correctly, users will observe an error stating that “the logon attempt failed” in the Windows 8 remote desktop client.
Load Balancing ChangesRD Gateway has another important feature called load balancing. The typical load balancing scenario consists of an RD Gateway farm with multiple RD Gateway servers. Previous versions of RD Gateway (Windows Server 2008 R2) support three types of load balancing mechanisms: Hardware, Software, and DNS Round Robin load balancing. All of the RD Gateway servers in the farm are used to load balance the end-user connections based on the traffic.
In Windows Server 2012, RD Gateway doesn’t support DNS Round Robin load balancing when used with the new HTTP transport, because this transport uses two HTTP channels (one for input and one for output) which must be routed to the same RD Gateway server (DNS Round Robin does not guarantee that both connections will be routed to the same server). However, hardware and software load balancers that support IP affinity, cookie-based affinity, or SSL ID-based affinity (and thus ensure that both HTTP connections are routed to the same server) can be used with RD Gateway. Furthermore, the UDP and HTTP connections may be handled by separate RD Gateway servers. Microsoft Network Load Balancing (NLB) supports IP affinity and thus can be used as a load balancer for RD Gateway.
Conclusion
RD Gateway in Windows Server 2012 offers new HTTP and UDP transports designed to allow remote users to take advantage of the WAN improvements in RDP 8.0 outside the corporate network. Take advantage of this support as well as the management console features, IIS configuration, and load balancing to provide a quality, scalable RDP 8.0 experience for your users!