Some of the more complicated support calls we see are related to Certificate Based Authentication (CBA) with ActiveSync. This post is intended to provide some clarifications of this topic and give you troubleshooting tips.
What is Certificate Based Authentication (CBA)? Instead of using Basic or WIA (Windows Integrated Authentication), the device will have a client (user) certificate installed, which will be used for authentication. The user will no longer have to save a password to authenticate with Exchange. This is not related to using SSL to connect to the server as we assume that you already have SSL setup. Also, just to be clear (as some people have those things confused) CBA is not two-factor authentication (2FA).
How does the client certificate get installed on the device? There’s several MDM (Mobile Device Management) solutions to install the client certificate on the device.
The most important part of working with CBA is to know where the client certificate will be accepted (or ‘terminated’). How you implement CBA will depend on the response to following questions:
- Will Exchange server be accepting the client certificate?
- Will an MDM or other device using Kerberos Constrained Delegation (KCD) be accepting the client certificate?
You can choose only one. You can’t have both Exchange and a device accepting the client certificate.
This post assumes that the user certificates have already been deployed in AD before CBA was implemented. The requirements for user certificates are documented here: Configure certificate based authentication in Exchange 2016.
If Exchange Server is accepting the client certificate
This configuration is simple and is fully documented in the following link that applies to Exchange 2013/2016. The configuration for legacy versions follows the IIS configuration steps. The overall functionality of CBA has not changed across versions however the requirements may vary.
Configuration of CBA is done via IIS Manager. The overall steps are: Installing Client Certificate Mapping Authentication feature on all CAS servers, enabling client certificate authentication, setting SSL client certificates to “required” and disabling other authentication methods and finally enabling client certificate mapping on the virtual directory,
- Configure certificate based authentication in Exchange 2016
- Configure certificate based authentication in Legacy versions
Important Notes:
- You cannot use multiple authentication methods and have client certificates enabled on the virtual directory. The client must either use client certificate or username and password to authenticate, not both.
- SSL settings should be set to “Require” not “Accept”. You can have connection failures if set improperly.
If MDM or another device is accepting the certificate and using KCD to authenticate the client device
What is important to note here is the client certificate will be accepted at the device, therefore, you would NOT configure client certificates on Exchange.
- Each vendor should have updated documentation to work with current Exchange version.
- To accept the client certificate, the MDM would require that KCD be configured to authenticate to Active Directory.
- Most vendors expect Windows Integrated Authentication configured on IIS/Exchange. This would allow the authentication to be passed without any additional prompts to the client device. All other authentication methods would be disabled.
Note: When you enable Integrated authentication on Exchange, you should ensure that the authentication “Providers” have both NTLM and Negotiate enabled in IIS Manager.
Overall authentication process when client certificate is accepted by MDM:
- The client device contacts MDM with a client certificate that contains UPN in the Subject Alternative Name section of the certificate
- The MDM authenticates the user with Active Directory
- KCD issues a Ticket to the MDM with user’s credentials
- MDM sends users credentials to Exchange with Windows Integrated (only) configured on Exchange.
- Exchange response to the MDM with the mail data.
- MDM responds to the client with mail data.
Coexistence with Exchange, when Exchange is accepting the client certificate
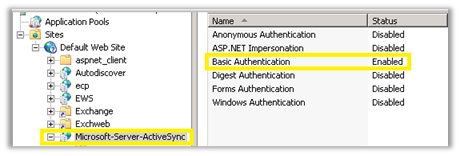
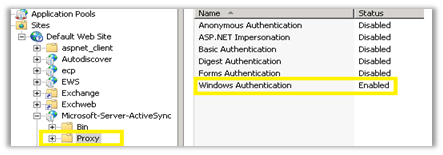
When adding 2013/2016 to the environment and Exchange server 2013/2016 is accepting the client certificate, it’s important to disable any client certificate configuration on the legacy CAS. This is because the client certificate will not be proxied to the legacy server. The authentication on Legacy CAS would go back to default of Basic on “Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync” virtual directory, and “Windows Integrated” on subfolder named “Proxy”.
Troubleshooting
Here are some troubleshooting steps!
If Exchange Server is accepting the client certificate
If Exchange is configured to accept the client certificate, use the IIS logs and look for requests for /Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync. Determine the error code that is returned. IIS error codes are found here.
- Verify the UPN configured on the “Subject Alternative Name” portion of the client certificate. In ADUC, click “View, Advanced Features”, locate the user account and select “Published Certificates”, click “Details” tab.
- Client certificates and SSL “Required” should not be enabled on the Default Web Site, only on the MSAS “Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync” virtual directory.
- Verify there are no additional authentication methods enabled on the MSAS virtual directory. See “Step 4” in Configure certificate based authentication in Exchange 2016
If MDM is accepting client certificate
- With MDM vendor, verify that KCD is working correctly, by checking security logs on MDM to verify Kerberos is working.
- Verify if the request is getting to Exchange by looking at the IIS logs requests for /Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync.
- Verify Windows Integrated (only) is enabled on Exchange.
Attachments
If users have issues with attachments, follow “Step 7” in Configure certificate based authentication in Exchange 2016
Troubleshooting Logs and Tools
Use the IIS logs to determine if the device reached the Exchange server. Look for requests to /Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync virtual directory.
Refer to The HTTP status code in IIS 7.0, IIS 7.5, and IIS 8.0 KB for information on the various error codes in the IIS logs. Example of IIS error code: 403.7 - Client certificate required. From this you would verify that the device has the client certificate installed.
- IIS Logs - IIS logs can be used to review the connection for Microsoft-Server-ActiveSync. More info here.
- Log Parser Studio - Log Parser Studio is a GUI for Log Parser 2.2. LPS greatly reduces complexity when parsing logs. Download it here
I wanted to thank Jim Martin for technical review of this post.
Charlene Stephens (Weber)