- Home
- Security, Compliance, and Identity
- Microsoft Sentinel Blog
- Identifying Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) Phishing Attacks through 3rd-Party Network Detection
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) phishing attacks represent an emerging and concerning trend, surpassing conventional phishing methods in their sophistication. These attacks possess the capability to maneuver around the security measures of multifactor authentication (MFA) by leveraging reverse-proxy functionality.
One prominent actor, identified as DEV-1101 and tracked by Microsoft, stands responsible for the development, facilitation, and promotion of various AiTM phishing kits. These kits are made available for purchase or rental, enabling other cybercriminals to perpetrate sophisticated phishing attacks. The accessibility of such kits in the criminal underground further industrializes the cybercrime economy, subsequently lowering the entry barrier for cybercriminal activities.
Detecting and mitigating the threats posed by AiTM phishing necessitates advanced monitoring techniques within 3rd-party networks. By delving into the artifacts obtained from 3rd-party network logs, we can unveil the footprints left by these sophisticated attacks. Understanding these artifacts is vital for proactive identification and response to AiTM phishing attempts, bolstering cybersecurity measures against this evolving threat landscape.
Why AiTM 3P Detection Required
In our previous blog series, we delved into a large-scale phishing campaign. These sophisticated tactics involved the creation of fraudulent sites that intercepted user login credentials, allowing attackers to hijack sign-in sessions and bypass authentication protections. Even users with enabled Multifactor Authentication (MFA) fell victim to this method.
The related blogs covered the intricacies of this campaign, shedding light on the evolving landscape of cyber threats and the critical importance of safeguarding against AiTM phishing attacks.
- Blog : Detecting and mitigating a multi-stage AiTM phishing and BEC campaign | Microsoft Security Blog
- Blog : Automatically disrupt adversary-in-the-middle attacks with XDR (microsoft.com)
- Blog : DEV-1101 enables high-volume AiTM campaigns with open-source phishing kit | Microsoft Security Blog
Impact of AiTM Attack:
Tools : Evilginx2, Modlishka, and Muraena.
- Session Cookie Hijacking: AiTM phishing seeks to obtain a user's session cookie, enabling attackers to bypass authentication processes. By intercepting the session cookie, the attacker gains access to the ongoing authenticated session without the need for supplying their own credentials.
- Authentication Bypass and MFA Evasion: The stolen session cookie enables attackers to skip the authentication process, even when users have Multifactor Authentication (MFA) enabled. This means that security measures like MFA are circumvented, allowing unauthorized access.
- Aspects of AiTM impact and capability: The AiTM phishing attack has been automated using tools such Evilginx2, Modlishka, and Muraena, indicating that these attacks executed efficiently at scale with widely available kits.
- Targeted Organizations and Post-Breach Activities: Microsoft 365 Defender detected AiTM phishing campaigns targeting over 10,000 organizations in the wild, in the Post-breach activities observed data enumeration in mailboxes and fraudulent financial transactions.
- Post-Breach Business Email Compromise (BEC): Once gaining unauthorized access, the attackers initiated a malicious tactic known as Business Email Compromise (BEC). Their objective was to manipulate finance-related emails in order to deceive their targets into transferring payments to accounts controlled by the attackers themselves. To evade detection, the attackers implemented various tactics. They manipulated the Inbox rules to conceal any suspicious activities and deleted evidence of their initial phishing email. By doing so, they aimed to avoid raising any red flags. Furthermore, the attackers displayed persistence by engaging with multiple targets within the compromised mailbox. They manipulated replies and adjusted the Inbox rules to deceive multiple targets simultaneously, amplifying the impact of their fraudulent activities.
- Immediate Action After Session Theft: Analysis revealed that attackers acted within minutes of stealing session cookies, launching suspicious activities and replying to ongoing financial threads within the compromised mailbox.
- Mitigation: Microsoft 365 Defender and Microsoft Sentinel plays a crucial role in detecting and responding to AiTM phishing attacks by integrating multiple solutions and offering comprehensive alert correlation to counter evolving threats.
Microsoft Sentinel And Microsoft 365 Defender Rules to Detect AiTM Phishing Events
Microsoft Sentinel, a cloud-native SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solution, provides a powerful framework for detecting and responding to security threats. To detect AiTM phishing attack from the 3P (Third Party) vendors like PaloAlotoNetworks, Fortinet, Microsoft Sentinel has published several Out-Of-The-Box (OOTB) detections and hunting queries available via the Content Hub within the product, which are specifically designed to identify and respond to suspicious activities related to AiTM attacks. Below, we'll discuss three key rules and explain how they work:
Rule 1: Phishing Link Clicks in Network Traffic.
- Description: This rule is designed to identify successful phishing link clicks by users and the subsequent network activity from non-Microsoft network devices.
- How it works: It identifies phishing-related alerts in Microsoft 365 Defender and matches them with 3rd party network device logs such as Firewalls instead non Microsoft devices. It aims to detect successful phishing link clicks followed by suspicious network activity.
Rule 2: Correlating M365D Alerts with Non-Microsoft Network Device Activity
- Description: This rule correlates Microsoft 365 Defender phishing-related alerts with sign-in activities on non-Microsoft network devices, especially when users connect to phishing URLs.
- How it works: It correlates Microsoft 365 Defender alerts with network logs from devices like Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, Check Point, and Zscaler. It focuses on cases where users connect to phishing URLs from these devices and subsequently make successful sign-in attempts.
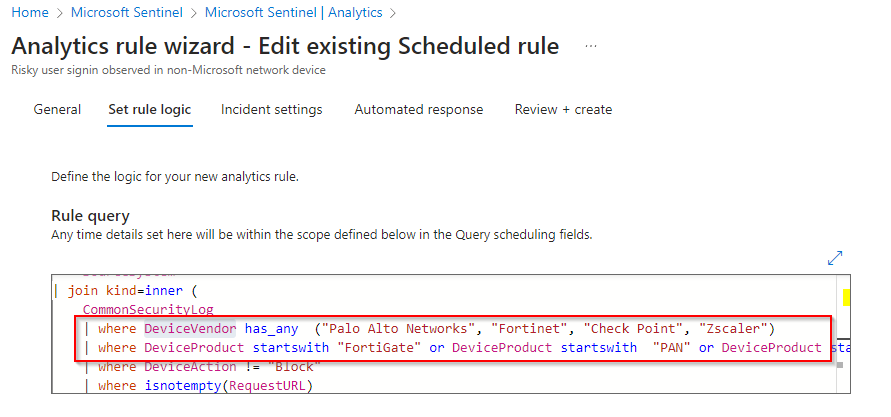
Rule 3: Risky User SignIn on Non-Microsoft Network Devices
- Description: This rule identifies successful logins by risky users on non-Microsoft network devices. It looks for users who have engaged in potentially suspicious network activity on these devices.
- How it works: By analyzing Azure Active Directory and security logs from network devices like Palo Alto Networks, Fortinet, Check Point, and Zscaler, this rule identifies suspicious user sign-ins. It then correlates these sign-ins with risky network activity.
Microsoft 365 Defender AiTM Detections:
The automatic attack disruption feature in Microsoft's XDR does not necessitate pre-configuration by the SOC team, it is inherently integrated. The following detections are enabled for automatic attack disruptions:
- User compromised via a known AiTM phishing kit
- User compromised in an AiTM phishing attack
- Stolen session cookie used
- Possible AiTM phishing attempt in Okta
The following reference blogs describe how we can utilize 3rd-party network signals and integrate it with Microsoft 365 Defender detections :
- From cookie theft to BEC: Attackers use AiTM phishing sites as entry point to further financial frau...
- Automatically disrupt adversary-in-the-middle attacks with XDR (microsoft.com)
- DEV-1101 enables high-volume AiTM campaigns with open-source phishing kit | Microsoft Security Blog
- Detecting and mitigating a multi-stage AiTM phishing and BEC campaign | Microsoft Security Blog
Linking Alerts to SOAR Playbooks in Microsoft Sentinel:
Explore these sample SOAR playbook scenarios, illustrating how the mentioned alerts can seamlessly connect to automated measures for early-stage attack disruption. Utilize Microsoft Sentinel's SOAR service with these playbooks to effectively counter AiTM phishing attacks by implementing automated actions against users and IPs based on the described detection methods.
Automated Threat Response with Microsoft Sentinel Playbooks:
Microsoft Sentinel offers a wealth of pre-built playbooks designed to automate responses to triggered alerts, providing an automated disruption feature crucial for halting ongoing attacks and streamlining the remediation and sanitization of enterprise environments.
For instance, leveraging the above AiTM rules, we can take advantage of 3P disruption capabilities from Palo Alto PAN-OS, Fortinet FortiGate, Check Point and Zscaler solution. These 3P solutions empower automated blocking of malicious IPs and URLs the moment the corresponding analytical rule is triggered. To configure playbooks that respond to analytical rules identifying malicious IP and URL entries in the entity list, organizations can efficiently leverage the existing wealth of pre-built playbooks for disruption within Microsoft Sentinel.
Create Your Own Custom Playbooks for Disruption:
Designing your personalized disruption strategies with Microsoft Sentinel Analytical Rules.
Trigger:
- Alert from Rule 1: Phishing Link Clicks in Network Traffic
- Alert from Rule 2: Correlating M365D Alerts with Non-Microsoft Network Device Activity
- Alert from Rule 3: Risky User SignIn on Non-Microsoft Network Devices
Actions:
- Disable the compromised user account in Active Directory and Azure Active Directory.
- Revoke the stolen session cookie to prevent the attacker from using it for additional malicious activity.
- Block the malicious IP address from accessing your organization's network.
- Quarantine the device used by the compromised user.
- Notify the user of the incident and provide them with instructions on how to reset their password.
- Investigate the incident to determine the scope of the attack and identify any other affected users or devices.
- Remediate the attack by removing any malicious actors from your network and restoring compromised systems.
- Update security policies and procedures to prevent similar attacks from happening in the future.
- Communicate the incident to your stakeholders and provide them with recommendations on how to protect themselves from AiTM phishing attacks.
Unlock the potential of Microsoft Sentinel's dynamic playbooks in your organization's security arsenal. These playbooks aren't just tools; they're a launchpad for your creativity. Tailor them to your organization's unique needs, using them as a foundation that aligns seamlessly with your security requirements. Dive in to Respond to Threats by Using Playbooks with Automation Rules in Microsoft Sentinel documentation to craft playbooks that go beyond the standard, addressing the distinct needs of your environment. This customization grants you the ability to elevate threat response mechanisms and seamlessly integrate disruption capabilities that fortify your security posture.
Microsoft Sentinel's playbooks offer unparalleled flexibility, allowing you to not only build upon existing frameworks but also to curate a threat response strategy that perfectly syncs with the nuanced intricacies of your organization's evolving security landscape.
How These Rules Help You Detect AiTM Attacks
These Microsoft Sentinel rules expand visibility by including 3rd party network data sources. By analyzing a wide range of data sources and employing advanced correlation techniques, they provide insights that help you detect AiTM phishing events early. Here's how they can benefit your organization:
- Early Detection: These rules help you detect AiTM attacks in their early stages, minimizing potential damage.
- Accurate Alerts: By correlating data from multiple sources, these rules reduce false positives and provide more accurate alerts.
- Timely Response: With real-time alerting and investigation capabilities, you can respond quickly to mitigate threats.
- Comprehensive Protection: These rules cover a wide range of network devices and data sources, offering comprehensive protection against AiTM attacks.
AiTM attacks are a growing concern in the cybersecurity landscape. Microsoft Sentinel's rules for AiTM attack detection provide valuable tools to safeguard your organization's data and infrastructure. Leveraging these rules and continually updating your security posture is crucial to staying one step ahead of evolving threats.
Customize the Rules to add additional 3p network vendors for monitoring.
To fortify your organization's security against AiTM phishing Attack and evolving cyber threats, customizing analytical rules is imperative. This process extends your defense capabilities, especially in onboarding additional 3rd party vendors within the existing rule framework. Follow these steps to adapt and enhance the rules for a more comprehensive coverage:
- Access Rule Templates: Once the rule templates are deployed, navigate to the editing feature within the system.
- Locate Rule Logic: Go to the rule logic section to explore and understand the underlying query logic. The "Rule query" section provides insight into the current logic applied.
- Identify Device Vendor and Product Lines: Within the "Rule query," locate the segments where "DeviceVendor" and "DeviceProduct" are configured. These parameters are typically crucial in identifying and flagging specific devices or products associated with potential threats
- Verify Compatibility and Datatype: Ensure that the added or modified vendor data sources and required the data connected is well configured in Microsoft Sentinel portal and validate the logs in Log analytics tables.
By using this Best practices for Microsoft Sentinel | Microsoft Learn , About Microsoft Sentinel content and solutions | Microsoft Learn, you can effectively customize analytical rules to extend coverage, enhancing your organization's defense against AiTM phishing and emerging cyber threats. Continual adaptation and vigilance are essential to staying ahead in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.