- Home
- Security, Compliance, and Identity
- Security, Compliance, and Identity
- New Blog Post | The many lives of BlackCat ransomware
New Blog Post | The many lives of BlackCat ransomware
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark Discussion as New
- Mark Discussion as Read
- Pin this Discussion for Current User
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Mark as New
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Mute
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Permalink
- Report Inappropriate Content
Jun 13 2022 01:14 PM
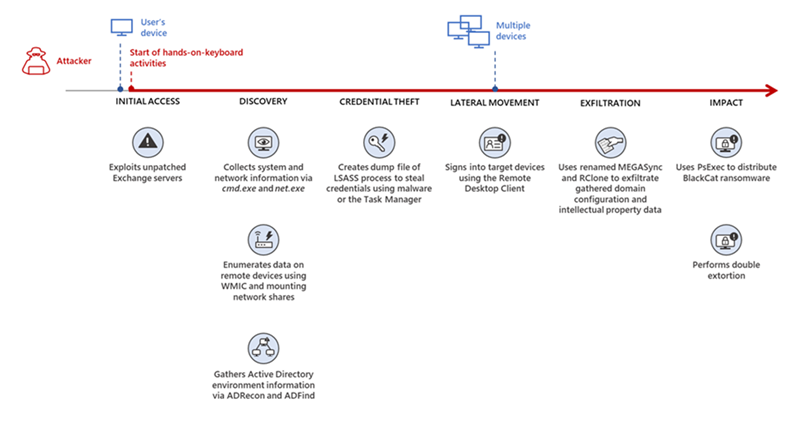
The many lives of BlackCat ransomware - Microsoft Security Blog
The BlackCat ransomware, also known as ALPHV, is a prevalent threat and a prime example of the growing ransomware-as-a-service (RaaS) gig economy. It’s noteworthy due to its unconventional programming language (Rust), multiple target devices and possible entry points, and affiliation with prolific threat activity groups. While BlackCat’s arrival and execution vary based on the actors deploying it, the outcome is the same—
First observed in November 2021, BlackCat initially made headlines because it was one of the first ransomware families written in the Rust programming language. By using a modern language for its payload, this ransomware attempts to evade detection, especially by conventional security solutions that might still be catching up in their ability to analyze and parse binaries written in such language. BlackCat can also target multiple devices and operating systems. Microsoft has observed successful attacks against Windows and Linux devices and VMWare instances.
- Labels:
-
Cloud Security