- Home
- Microsoft Intune and Configuration Manager
- Intune Customer Success
- Microsoft Intune Public Preview - Windows 10 Device diagnostics
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
By Jon Lynn – Sr. Service Engineer | Microsoft Endpoint Manager – Intune
Updated 7/29/21: We're excited to share that the Windows 10 Device diagnostics feature is now generally available! See our What’s New in Microsoft Endpoint Manager - 2107 (July) Edition post to learn more. You can also see it in action here.
In our 2102 (February) Microsoft Intune service release we are enabling a public preview of the Windows 10 Device diagnostics feature. We’ve listened to your feedback and understand that troubleshooting, especially with the emphasis on remote work, can be particularly challenging. This first release of device diagnostics utilizes the Windows DiagnosticLog CSP, allowing Intune to collect a set of files, registry, event viewers and commands to be gathered on a Windows 10 or a Microsoft HoloLens 2 device. The diagnostic process is quite easy, fast, and reliable, generally taking about 5 minutes from start to finish.
Let’s take a look at the requirements to use device diagnostics:
Client requirements
- Desktop: Windows 10 1909 / 19H2 or later (build number 10.0.18363+) – Home, Pro, Enterprise and Education versions supported.
- HoloLens 2: Windows 10 2004 / 20H1 or later (build number 10.0.19041+).
- Device must be online, be available via the internet and Windows Push Notification Service (WNS) must have access to the machine.
Intune requirements
- To initiate a device diagnostics, you must be assigned to a Global Admin role, Intune Admin role, School Administrator, Help Desk Operator, or have the Collect diagnostics permission assigned to a custom role.
- The device you’d like to collect diagnostics from must be designated as Corporate-Owned.
Once the client and Intune requirements are met, simply navigate in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center to the Devices > All Devices blade and search for the device you want to collect diagnostics on.
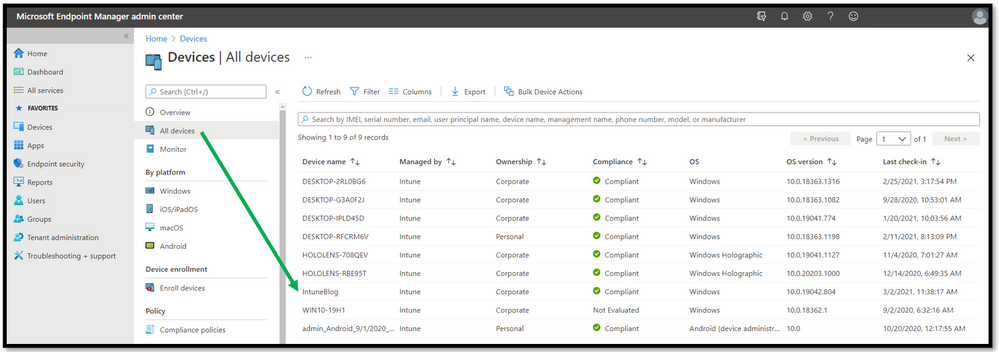
Double click on the device and choose the device action “Collect diagnostics”.

The status and results of the Collect diagnostics task can be found under Device diagnostics (Preview). Once opened, the monitor displays who ran the Collect diagnostics task, status, when it was started, when diagnostics were uploaded, and a download button when complete (if successful).
There are three status messages for a diagnostic task, let us review each:
- Completed: Diagnostics were successful and are available for download.
- Pending diagnostics Upload: The device is running the diagnostics and will finish shortly, or the device is offline/unreachable and has not received the request. The diagnostics task is good for 12 hours, so if the machine comes online and/or checks into the Intune service, the diagnostic action will be kicked off.
- Failed: The device ran diagnostics but failed to complete the task or failed to upload. To troubleshoot this issue, please review the MDMDiagnostics registry key at HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\MdmDiagnostics and the sub keys inside. If collecting diagnostics fails, we recommend you run the device action again. If it continues to fail, please open a case with Intune support from the Endpoint Manager admin center.
Here’s what a pending and completed diagnostic collection status looks like:
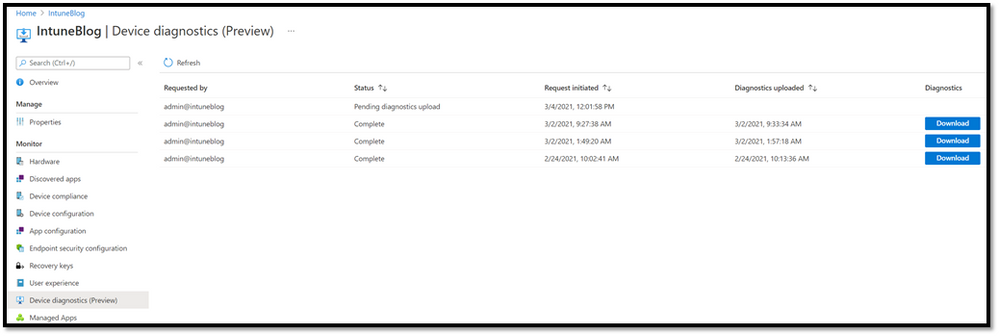
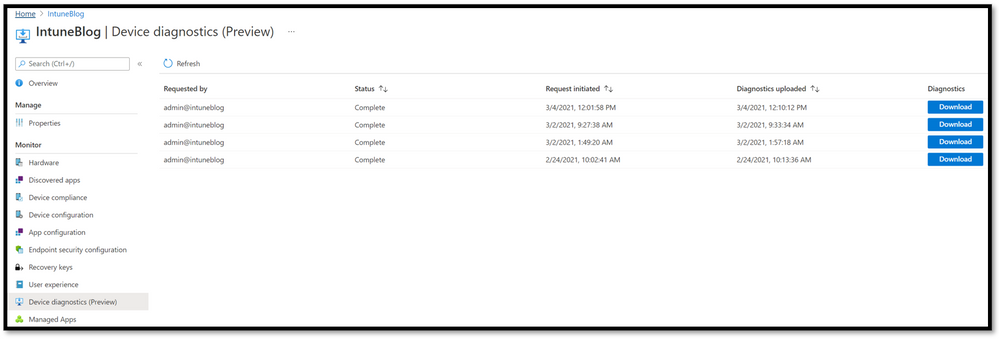
Now that the diagnostic has completed, click download, save to your machine, and extract the zip file. You will know notice the zip file has many folders. This can be confusing and unfortunately, it’s not something we can change because that is how the DiagnosticLog CSP handles the files. However, we are working on an update to flatten the folders and simplify the process after diagnostics are gathered. To help simplify the diagnostics during the preview, please see the PowerShell script provided later in the blog.
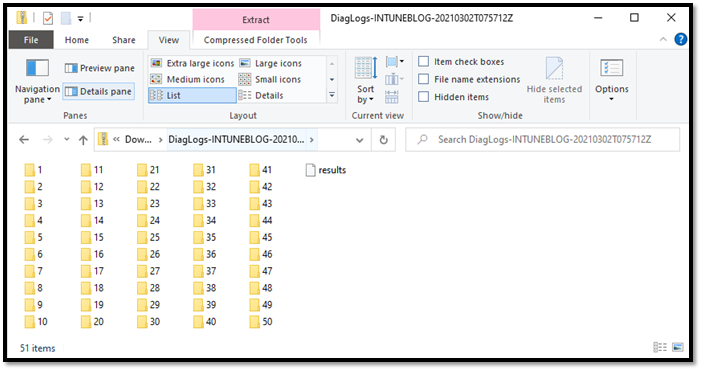
Each file, command, registry, or event viewers is stored in an individual folder to be compressed into a zip file, see the image below for a sample of the zip and contents.
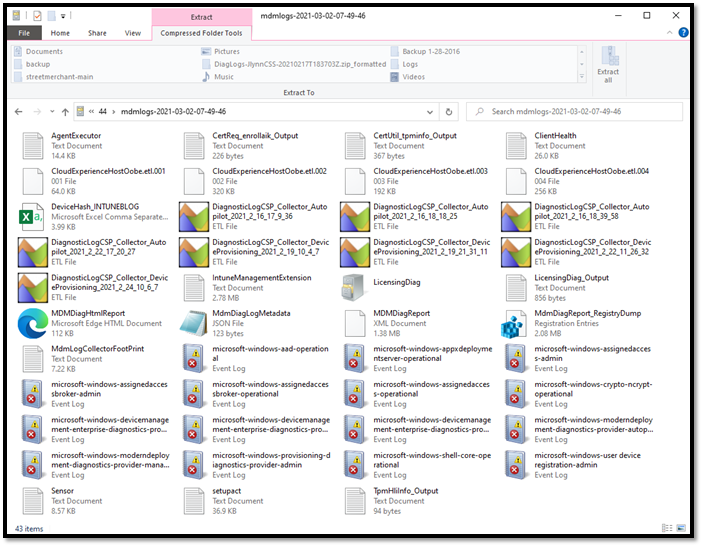
Now that we have reviewed how to collect diagnostics, let’s review what we are collecting from machines. Currently we collect useful registry keys, command outputs, MDM diagnostic logs and other critical Microsoft data like Microsoft Defender ATP logs.
Also, it is important to note, there are restrictions on what and where we can gather data using the DiagnosticLog CSP. We cannot collect information from user data folders, nor non-diagnostic file types, like photo or document file types. I highly encourage you to review the DiagnosticLog CSP documentation here for all the details. Microsoft personnel may access device diagnostics to assist in troubleshooting and resolving incidents. The logs are encrypted at rest after uploading them.
Here is the standard diagnostics template Intune is collecting and what it’s useful for:
Windows 10 Desktop OS:
- HKLM\Software\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension
- This registry key contains specific information about the Intune Management Extension.
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\SystemCertificates\AuthRoot
- This registry key contains info about certificates installed on your machine.
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows Advanced Threat Protection
- This registry key contains detailed info on your Microsoft Defender ATP configuration.
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Authentication\LogonUI
- This registry key contains the last logged on user.
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Internet Settings
- This registry key contains info on your Internet configuration.
- HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
- This registry key contains the 32-bit applications that are installed on the machine.
- HKLM\Software\Policies
- This registry key contains information on the policies configured on the machine.
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Cryptography\Configuration\SSL
- This registry key contains more information on certificates.
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows Advanced Threat Protection
- This registry key contains policy information related to Microsoft Defender ATP.
- HKLM\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall
- This registry key contains the 64-bit applications that are installed on the machine.
- HKLM\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Control\SecurityProviders\SCHANNEL
- This registry key contains information on the TLS configuration on the machine.
Commands:
- %programfiles%\windows defender\mpcmdrun.exe -GetFiles
- The command captures support data for troubleshooting ATP issues.
- %windir%\system32\certutil.exe -store
- This command outputs the certificates installed on the machine’s store.
- %windir%\system32\certutil.exe -store -user my
- This command outputs the certificates installed on the machine’s user store.
- %windir%\system32\Dsregcmd.exe /status
- This command outputs Azure AD information for the machine.
- %windir%\system32\ipconfig.exe /all
- This command outputs the IP address information for the machine.
- %windir%\system32\mdmdiagnosticstool.exe -area Autopilot;deviceprovisioning;deviceenrollment;tpm;HololensFallbackDeviceOwner -cab %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\mdmlogs-<Date/Time>.cab
- This command captures MDM diagnostics for the machine.
- %windir%\system32\msinfo32.exe /report %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\msinfo32.log
- This command outputs the hardware, software and driver details for the machine.
- %windir%\system32\netsh.exe advfirewall show allprofiles
- This command outputs the firewall configuration for all profiles.
- %windir%\system32\netsh.exe advfirewall show global
- This command outputs the global firewall configuration.
- %windir%\system32\netsh.exe lan show profiles
- This command outputs the configuration of the LAN Adapter(s).
- %windir%\system32\netsh.exe winhttp show proxy
- This command outputs network proxy configuration.
- %windir%\system32\netsh.exe wlan show profiles
- This command outputs the proxy configuration of the Wireless LAN Adapters(s).
- %windir%\system32\netsh.exe wlan show wlanreport
- This command outputs the status of the Wireless LAN.
- %windir%\system32\ping.exe -n 50 localhost
- This command runs a test of the local network host.
- %windir%\system32\powercfg.exe /batteryreport /output %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\battery-report.html
- This command generates a detailed report about day-to-day battery usage.
- %windir%\system32\powercfg.exe /energy /output %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\energy-report.html
- This command generates a Battery Report, useful for troubleshooting laptop battery/power issues.
Event Viewers: We are capturing the common event viewers for troubleshooting issues, including Application, System and Setup. In addition, we are capturing the AppLocker event viewers to assist in debugging AppLocker issues and the SENSE event viewers to help debugging issues with anti-virus/malware.
- Application
- Microsoft-Windows-AppLocker/EXE and DLL
- Microsoft-Windows-AppLocker/MSI and Script
- Microsoft-Windows-AppLocker/Packaged app-Deployment
- Microsoft-Windows-AppLocker/Packaged app-Execution
- Microsoft-Windows-Bitlocker/Bitlocker Management
- Microsoft-Windows-SENSE/Operational
- Microsoft-Windows-SenseIR/Operational
- Setup
- System
Files: These commands collect the files generated during the log collection and files on the machine used for debugging issues. We are capturing all the data mentioned earlier along with Configuration Manager setup and client logs, CBS logs for issues and measured boot ETL’s to assist in machine security issues.
- %ProgramData%\Microsoft\DiagnosticLogCSP\Collectors\*.etl
- %ProgramData%\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs\*.*
- %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows Defender\Support\MpSupportFiles.cab
- %ProgramData%\Microsoft\Windows\WlanReport\wlan-report-latest.html
- %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\battery-report.html
- %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\energy-report.html
- %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\mdmlogs-<Date/Time>.cab
- %temp%\MDMDiagnostics\msinfo32.log
- %windir%\ccm\logs\*.log
- %windir%\ccmsetup\logs\*.log
- %windir%\logs\CBS\cbs.log
- %windir%\logs\measuredboot\*.*
- %windir%\Logs\WindowsUpdate\*.etl
HoloLens 2:
Commands:
- %windir%\system32\mdmdiagnosticstool.exe -area Autopilot;deviceprovisioning;deviceenrollment;tpm;HololensFallbackDeviceOwner -zip %programdata%\MDMDiagnostics\mdmlogs-DATE/TIME.zip
Folders/Files:
-
%programdata%\MDMDiagnostics\mdmlogs-<Date/Time>.zip
-
%ProgramData%\Microsoft\DiagnosticLogCSP\Collectors\*.etl
-
%windir%\logs\measuredboot\*.*
For the public preview we have created a PowerShell script that will take the downloaded zip file and convert it into a simplified folder file with updated file names to describe each one and removing all the folders.
To use the PowerShell script, simply open a PowerShell prompt, and use the name of the download file as the input for the script.
Example: Devicediagnostics.ps1 Download.zip
Device diagnostics PowerShell Script:
param($DiagnosticArchiveZipPath)
#region Formatting Choices
$flatFileNameTemplate = '({0:D2}) {1} {2}'
$maxLengthForInputTextPassedToOutput = 80
#endregion
#region Create Output Folders and Expand Zip
$diagnosticArchiveTempUnzippedPath = $DiagnosticArchiveZipPath + "_expanded"
if(-not (Test-Path $diagnosticArchiveTempUnzippedPath)){mkdir $diagnosticArchiveTempUnzippedPath}
$reformattedArchivePath = $DiagnosticArchiveZipPath + "_formatted"
if(-not (Test-Path $reformattedArchivePath)){mkdir $reformattedArchivePath}
Expand-Archive -Path $DiagnosticArchiveZipPath -DestinationPath $diagnosticArchiveTempUnzippedPath
#endregion
#region Discover and Move/rename Files
$resultElements = ([xml](Get-Content -Path (Join-Path -Path $diagnosticArchiveTempUnzippedPath -ChildPath "results.xml"))).Collection.ChildNodes | Foreach-Object{ $_ }
$n = 1
# only process supported directives
$supportedDirectives = @('Command', 'Events', 'FoldersFiles', 'RegistryKey')
foreach( $element in $resultElements) {
# only process supported directives, skip unsupported ones
if(!$supportedDirectives.Contains($element.Name)) { continue }
$directiveNumber = $n
$n++
$directiveType = $element.Name
$directiveStatus = [int]$element.Attributes.ItemOf('HRESULT').psbase.Value
$directiveUserInputRaw = $element.InnerText
# trim the path to only include the actual command - not the full path
if ($element.Name -eq 'Command') {
$lastIndexOfSlash = $directiveUserInputRaw.LastIndexOf('\');
$directiveUserInputRaw = $directiveUserInputRaw.substring($lastIndexOfSlash+1);
}
$directiveUserInputFileNameCompatible = $directiveUserInputRaw -replace '[\\|/\[\]<>\:"\?\*%\.\s]','_'
$directiveUserInputTrimmed = $directiveUserInputFileNameCompatible.substring(0, [System.Math]::Min($maxLengthForInputTextPassedToOutput, $directiveUserInputFileNameCompatible.Length))
$directiveSummaryString = $flatFileNameTemplate -f $directiveNumber,$directiveType,$directiveUserInputTrimmed
$directiveOutputFolder = Join-Path -Path $diagnosticArchiveTempUnzippedPath -ChildPath $directiveNumber
$directiveOutputFiles = Get-ChildItem -Path $directiveOutputFolder -File
foreach( $file in $directiveOutputFiles) {
$leafSummaryString = $directiveSummaryString,$file.Name -join ' '
Copy-Item $file.FullName -Destination (Join-Path -Path $reformattedArchivePath -ChildPath $leafSummaryString)
}
}
#endregion
Remove-Item -Path $diagnosticArchiveTempUnzippedPath -Force -Recurse
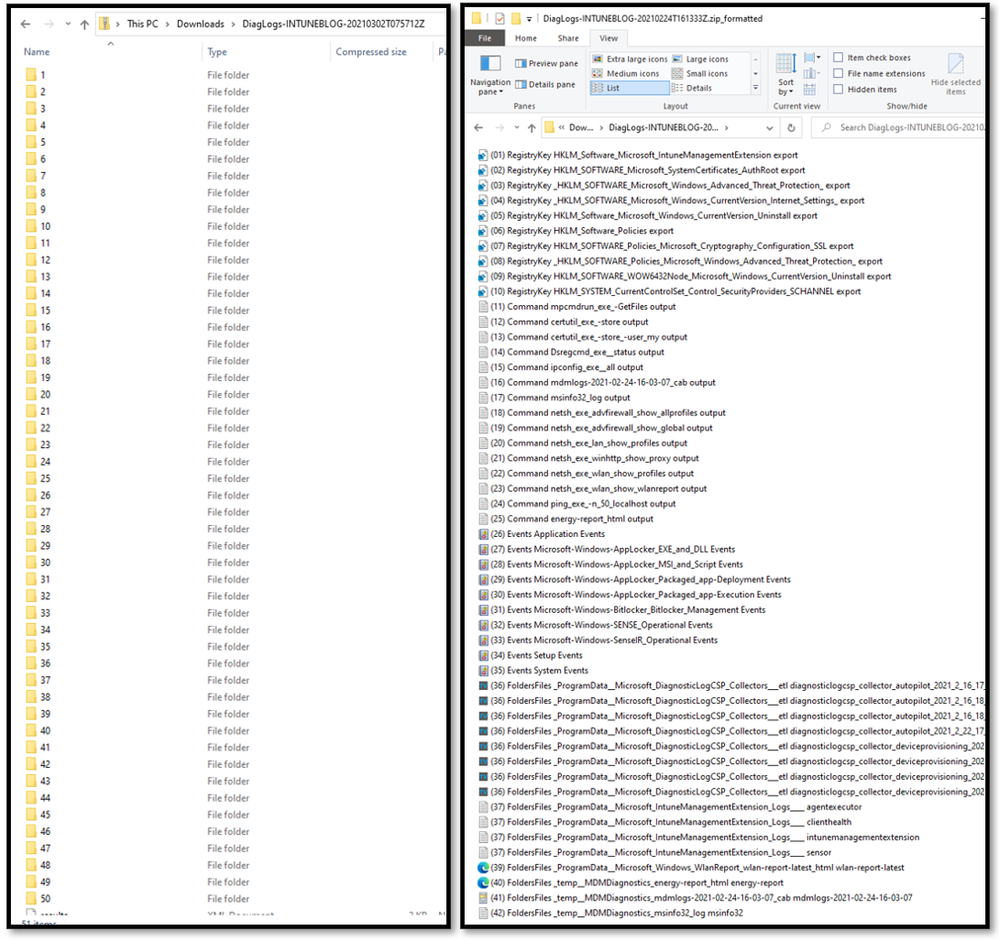
Standard Zip versus PowerShell converted folder:
Lastly, if your organization does not want to utilize device diagnostics and wants to prevent IT admins from collecting diagnostics, the feature can be completely disabled in the Tenant Administration workload in the Microsoft Endpoint Manager admin center. Navigate to Tenant Admin > Device diagnostics (Preview) and disable the feature. Only a global administrator or Intune administrator can make this change.

Frequently asked questions and known issues (FAQ):
- Unzipping diagnostics with 7Zip returns empty folders – This is a known issue with compressed files created by Windows and 7Zip. We recommend using a different tool to unzip the files.
- If uploading diagnostics to Intune takes more than 30 seconds, the diagnostic collection task will fail – This is a known issue with the DiagnosticLog CSP that has been fixed in KB4601315 and KB4601319, which were released on February 2th, 2021 via Windows Update. Please ensure your machines have been updated.
- Device diagnostics has been pending for a while, what should I do? – Best practice is to ensure the device can communicate with the service. Forcing a device check-in will ensure the device is able to reach the Intune service. If the device can reach the service, retry the diagnosticsaction.
- How long are the diagnostics available? – Diagnostics are available for download for 28 days and then automatically deleted per data retention requirements.
- How many diagnostics can I run on a device? – Each device may have up to 10 diagnostics. After 10, the oldest set of diagnostics is removed and replaced.
- What’s the maximum size of diagnostics I can collect? – 250mb of compressed files currently.
- Is this feature going to cost me anything? – No, the feature is included with your M365, Intune, EMS, or otherwise qualifying subscription.
We are excited to ship this feature and look forward to your feedback and comments. Let us know if you have any additional questions by replying to this post or reaching out to @IntuneSuppTeam on Twitter.
Post updates:
07/29/21: Windows 10 device diagnostics is now generally available!
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.