Create Virtual Network & Add Subnet
On the Azure portal menu or from the Home page, select Create a resource.
- Select Networking > Virtual network.
- For Subscription, select your subscription.
- For Resource group, select <jasparrow>.
- For Name, type Test-FW-VN.
- For Region, select the same location that you used previously.
- Select Next: IP addresses.
- For IPv4 Address space, type 10.0.0.0/16.
- Under Subnet, select default.
- For Subnet name type AzureFirewallSubnet. The firewall will be in this subnet, and the subnet name must be AzureFirewallSubnet.
- For Address range, type 10.0.1.0/26.
- Select Save.
Next, create a subnet for the workload server.
- Select Add subnet.
- For Subnet name, type Workload-SN.
- For Subnet address range, type 10.0.2.0/24.
- Select Add.
- Select Review + create.
- Select Create.
Create Virtual Machine
Now create the workload virtual machine, and place it in the Workload-SN subnet.
- On the Azure portal menu or from the Home page, select Create a resource.
- Select Compute and then select Virtual machine.
- Windows Server 2019 Datacenter in the Featured list.
- Enter these values for the virtual machine:
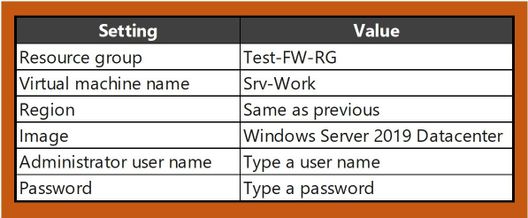
- Under Inbound port rules, Public inbound ports, select None.
- Accept the other defaults and select Next: Disks.
- Accept the disk defaults and select Next: Networking.
- Make sure that Test-FW-VN is selected for the virtual network and the subnet is Workload-SN.
- For Public IP, select None.
- Accept the other defaults and select Next: Management.
- Select Off to disable boot diagnostics. Accept the other defaults and select Review + create.
- Review the settings on the summary page, and then select Create.
Deploy Azure Firewall
- On the Azure portal menu or from the Home page, select Create a resource.
- Type firewall in the search box and press Enter.
- Select Firewall and then select Create.
- On the Create a Firewall page, use the following table to configure the firewall:
- Select Review + create.
- Review the summary, and then select Create to create the firewall.This will take a few minutes to deploy.
- After deployment completes, go to the <jasparrow> resource group, and select the Test-FW01 firewall.
- Note the firewall private and public IP addresses. You’ll use these addresses later.
Creating a Default Route
For the Workload-SN subnet, configure the outbound default route to go through the firewall.
- On the Azure portal menu, select All services or search for and select All services from any page.
- Under Networking, select Route tables.
- Select Add.
- For Name, type Firewall-route.
- For Subscription, select your subscription.
- For Resource group, select <jasparrow>.
- For Location, select the same location that you used previously.
- Select Create.
- Select Refresh, and then select the Firewall-route route table.
- Select Subnets and then select Associate.
- Select Virtual network > Test-FW-VN.
- For Subnet, select Workload-SN. Make sure that you select only the Workload-SN subnet for this route, otherwise your firewall won’t work correctly.
- Select OK.
- Select Routes and then select Add.
- For Route name, type fw-dg.
- For Address prefix, type 0.0.0.0/0.
- For Next hop type, select Virtual appliance.Azure Firewall is actually a managed service, but virtual appliance works in this situation.
- For Next hop address, type the private IP address for the firewall that you noted previously.
- Select OK.
Creating Application Rule
This is the application rule that allows outbound access to www.google.com.
- Open the <jasparrow>, and select the Test-FW01 firewall.
- On the Test-FW01 page, under Settings, select Rules.
- Select the Application rule collection tab.
- Select Add application rule collection.
- For Name, type App-Coll01.
- For Priority, type 200.
- For Action, select Allow.
- Under Rules, Target FQDNs, for Name, type Allow-Google.
- For Source type, select IP address.
- For Source, type 10.0.2.0/24.
- For Protocol:port, type http, https.
- For Target FQDNS, type www.google.com
- Select Add.
Creating Network Rule
This is the network rule that allows outbound access to two IP addresses at port 53 (DNS).
- Select the Network rule collection tab.
- Select Add network rule collection.
- For Name, type Net-Coll01.
- For Priority, type 200.
- For Action, select Allow.
- Under Rules, IP addresses, for Name, type Allow-DNS.
- For Protocol, select UDP.
- For Source type, select IP address.
- For Source, type 10.0.2.0/24.
- For Destination type select IP address.
- For Destination address, type 209.244.0.3,209.244.0.4These are public DNS servers operated by CenturyLink.
- For Destination Ports, type 53.
- Select Add.
Creating NAT Rule Testing Traffic
This rule allows you to connect a remote desktop to the Srv-Work virtual machine through the firewall.
- Select the NAT rule collection tab.
- Select Add NAT rule collection.
- For Name, type rdp.
- For Priority, type 200.
- Under Rules, for Name, type rdp-nat.
- For Protocol, select TCP.
- For Source type, select IP address.
- For Source, type *.
- For Destination address, type the firewall public IP address.
- For Destination Ports, type 3389.
- For Translated address, type the Srv-work private IP address.
- For Translated port, type 3389.
- Select Add.
DNS Configuration & Testing
For testing purposes in this tutorial, configure the server’s primary and secondary DNS addresses. This isn’t a general Azure Firewall requirement.
- On the Azure portal menu, select Resource groups or search for and select Resource groups from any page. Select the <jasparrow>resource group.
- Select the network interface for the Srv-Work virtual machine.
- Under Settings, select DNS servers.
- Under DNS servers, select Custom.
- Type 209.244.0.3 in the Add DNS server text box, and 209.244.0.4 in the next text box.
- Select Save.
- Restart the Srv-Work virtual machine.
Test the firewall
Now, test the firewall to confirm that it works as expected.
- Connect a remote desktop to firewall public IP address and sign in to the Srv-Work virtual machine.
- Open Internet Explorer and browse to https://www.google.com.
- Select OK > Close on the Internet Explorer security alerts.You should see the Google home page.
- Browse to https://www.microsoft.com.You should be blocked by the firewall.
So now you’ve verified that the firewall rules are working:
- You can browse to the one allowed FQDN, but not to any others.
- You can resolve DNS names using the configured external DNS server.
Reference