- Home
- Microsoft FastTrack
- FastTrack for Azure
- Azure VPN Gateway vs. ExpressRoute - Quick comparison
- Subscribe to RSS Feed
- Mark as New
- Mark as Read
- Bookmark
- Subscribe
- Printer Friendly Page
- Report Inappropriate Content
Table Of Contents
- Introduction
- VPN Gateway
- ExpressRoute Gateway
- Key differences table between P2S, S2S and ExpressRoute
Introduction
Let's start by clearing the confusion around the terms Virtual Network Gateway, VPN Gateway, and ExpressRoute Gateway.
-
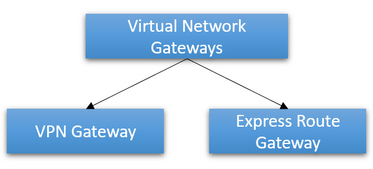
Virtual Network Gateway represents the category of gateways that reside inside a virtual network and are used to connect virtual networks or on-premises networks to virtual networks.
-
VPN Gateway is a specific type of Virtual Network Gateway. It is used to send encrypted traffic across the public Internet. Site-to-Site, Point-to-Site, and VNet-to-VNet connections all use a VPN gateway.
-
ExpressRoute Gateway is also a specific type of Virtual Network Gateway. It sends network traffic on a dedicated private connection when configuring Azure ExpressRoute.
When you create a Virtual Network Gateway, you need to specify several settings. One required setting -GatewayTypespecifies whether the gateway is used for ExpressRoute or VPN traffic. Each virtual network can have only one Virtual Network Gateway of each type. For example, you can have only one Virtual Network Gateway that uses -GatewayType VPN, and one that uses -GatewayType ExpressRoute.
VPN Gateway
A virtual network gateway is composed of two or more Azure-managed VMs automatically configured and deployed to a specific subnet you create called the GatewaySubnet. When you create a VPN gateway, gateway VMs are deployed to the gateway subnet and configured with your specified settings. This process can take 45 minutes or more to complete, depending on your selected gateway SKU.
Connectivity designs
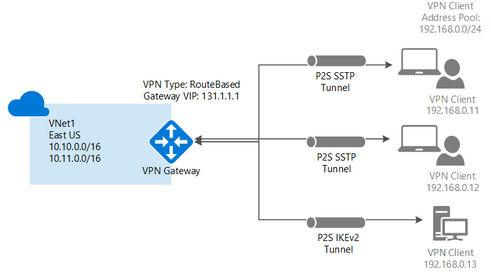
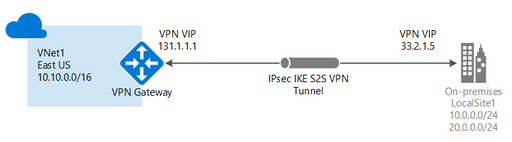
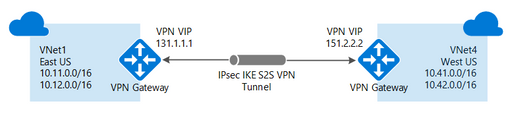
You can create multiple connection configurations using VPN Gateway, so you must determine which configuration best fits your needs. Point-to-Site (P2S), Site-to-Site (S2S), and VNet-to-VNet (V2V) connections all have different instructions and configuration requirements. See all details about the VPN Gateway designs here.
Point-to-Site (P2S)
Site-to-Site (S2S)
VNet-to-VNet (V2V)
ExpressRoute Gateway
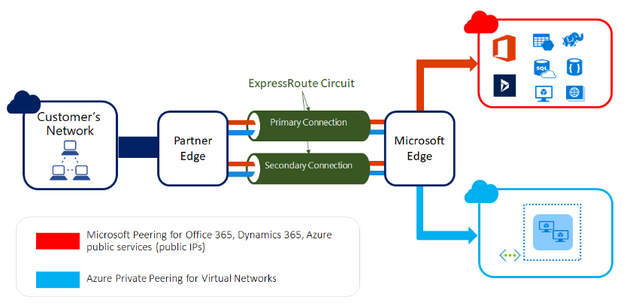
Azure ExpressRoute lets you extend your on-premises networks into the Microsoft cloud over a private connection with the help of a connectivity provider. With ExpressRoute, you can establish connections to Microsoft cloud services, such as Microsoft Azure and Microsoft 365.
You must first create a virtual network gateway to connect your Azure virtual network and your on-premises network using ExpressRoute. A virtual network gateway serves two purposes: exchanging IP routes between the networks and routing traffic.
Benefits of using Azure ExpressRoute
- Layer 3 connectivity between your on-premises network and the Microsoft Cloud through a connectivity provider. Connectivity can be from an any-to-any (IPVPN) network, a point-to-point Ethernet connection, or through a virtual cross-connection via an Ethernet exchange.
- Connectivity to Microsoft cloud services across all regions in the geopolitical region.
- Global connectivity to Microsoft services across all regions with the ExpressRoute premium add-on.
- Dynamic routing between your network and Microsoft via BGP.
- Built-in redundancy in every peering location for higher reliability.
- Connection uptime SLA.
- QoS support for Skype for Business.
Connectivity models
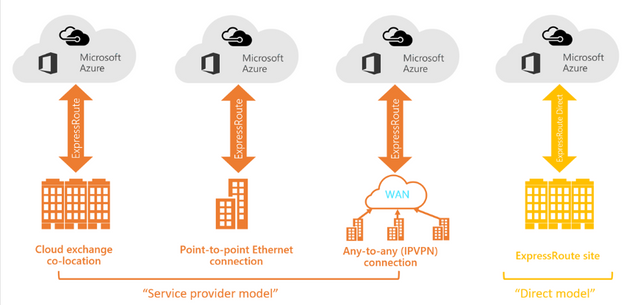
Connectivity can be from an any-to-any (IP VPN) network, a point-to-point Ethernet network, or a virtual cross-connection through a connectivity provider at a colocation facility. ExpressRoute connections don't go over the public Internet. This allows ExpressRoute connections to offer more reliability, faster speeds, consistent latencies, and higher security than typical connections over the Internet. For information on how to connect your network to Microsoft using ExpressRoute, see ExpressRoute connectivity models.
Key differences
The following table shows the main differences between Point-to-Site, Site-to-Site, and ExpressRoute at the time of this writing.
|
|
Point-to-Site |
Site-to-Site |
ExpressRoute |
|
Azure Supported Services |
Cloud Services and Virtual Machines |
Cloud Services and Virtual Machines |
|
|
Typical Bandwidths |
Based on the gateway SKU |
Typically < 10 Gbps aggregate |
50 Mbps, 100 Mbps, 200 Mbps, 500 Mbps, 1 Gbps, 2 Gbps, 5 Gbps, 10 Gbps, 100 Gbps |
|
Gateway SKU |
|||
|
Protocols Supported |
Secure Sockets Tunneling Protocol (SSTP), OpenVPN, and IPsec |
IPsec/ IKE |
Direct connection over VLANs, NSP's VPN technologies (MPLS, VPLS,...) |
|
Encryption |
|||
|
Routing |
RouteBased (dynamic) |
We support PolicyBased (static routing) and RouteBased (dynamic routing VPN) |
BGP |
|
Connection resiliency |
active-passive |
active-passive or active-active |
active-active |
|
High Availability |
- |
Highly Available cross-premises and VNet-to-VNet connectivity
|
Designing for high availability with ExpressRoute
|
|
Typical use case |
Secure access to Azure virtual networks for remote users
Reference architectures: |
Dev/test / lab scenarios and small to medium-scale production workloads for cloud services and virtual machines
Reference architectures: Hub-spoke network topology in Azure
|
Access to all Azure services (validated list), Enterprise-class and mission-critical workloads, Backup, Big Data, Azure as a DR site
Reference architectures: Extend an on-premises network using ExpressRoute Connect an on-premises network to Azure using ExpressRoute with VPN failover |
|
SLA |
99.9% availability for each Basic Gateway for VPN 99.95% availability for all Gateway for VPN SKUs, excluding Basic. |
99.9% availability for each Basic Gateway for VPN 99.95% availability for all Gateway for VPN SKUs, excluding Basic. |
99.9% availability for Basic Gateway for ExpressRoute. 99.95% availability for all Gateway for ExpressRoute SKUs, excluding Basic. |
|
Pricing |
A combination of VPN Gateway type and data transfer. Each type supports different bandwidth and number of tunnels. |
A combination of VPN Gateway type and data transfer. Each type supports different bandwidth and number of tunnels. |
A combination of the metered data plan for the outbound transfers and the gateway type. |
|
Technical Documentation |
|||
|
FAQ |
You must be a registered user to add a comment. If you've already registered, sign in. Otherwise, register and sign in.